Google changes Core Web Vitals metrics; How to use lab and field data for optimization
Field data, considered towards rankings, will vary depending on real-world user device power, screen size, and network connectivity. Lab data has default values for these and, (except in the case of Page Speed Insights), can be calibrated by developers to simulate all manner of conditions.
Google’s mobile page experience ranking factor, originally thought to be part of May’s Core Ranking Update, will be rolling out in a matter of days. .... There are several weeks reserved for observation and adjustment: “Page experience won’t play its full role as part of those systems until the end of August,” said Google. After that, the desktop page experience ranking factor will be next to roll out and will be fully launched before the end of the year.
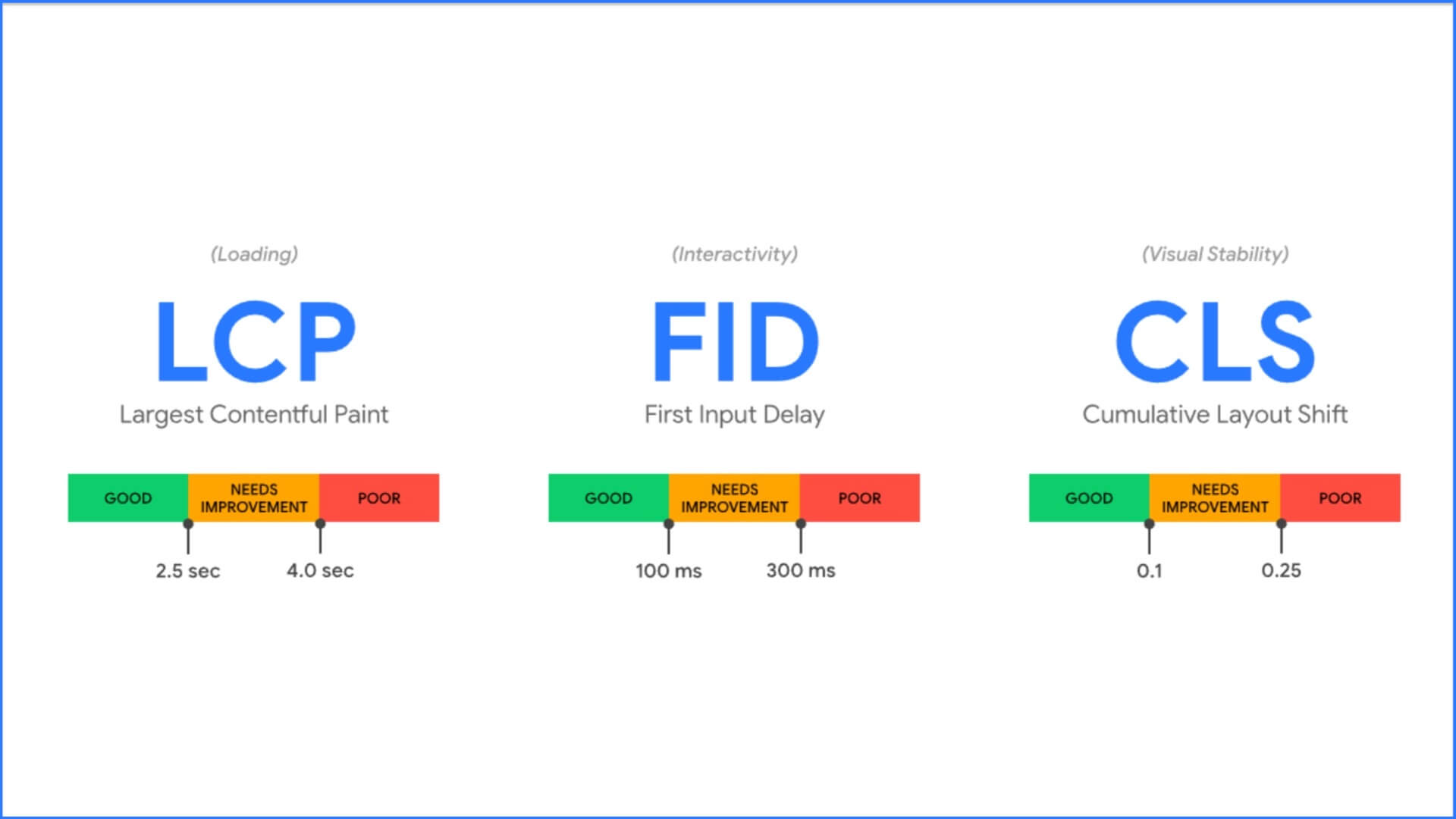
Core Web Vitals performance metrics are complex and imperfect, and fixing page experience snags can be perplexing. Even now, Google made last-minute changes for upgrading all its tools to include sharpened formulas in response to cases brought by developers in the field. .... You can generally look forward to improved scores if you have been affected by the metrics which have undergone some reengineering. Particularly helpful are modifications to the way Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) are measured.
Changes to First Contentful Paint
The threshold for achieving “good” scores for First Contentful Paint (FCP), a proxy metric that contributes to Core Web Vitals without actually being one, increased from 1.0 to 1.8 seconds. FCP accounts for Time to First Byte, more a reflection of your server response time than anything you manipulate directly with code, plus the time it takes to process render blocking resources such as CSS, which you can.
Changes to Largest Contentful Paint
LCP, a significant milestone in the lifecycle of a page, originally didn’t include some offscreen elements. Now LCP pinpoints the largest element even if after it is later removed from the page DOM once discovered, or when several images of the same size all qualify. Such situations occur when carousels load and cache content for offscreen slides. Another helpful modification is background images get ignored by LCP, as well.
Lots more information in the source article...